知彼知己方能百战百胜,用 Spring Security 来满足我们的需求最好了解其原理,这样才能随意拓展,本篇文章主要记录 Spring Security 的基本运行流程。
过滤器
Spring Security 基本都是通过过滤器来完成配置的身份认证、权限认证以及登出。
Spring Security 在 Servlet 的过滤链(filter chain)中注册了一个过滤器 FilterChainProxy,它会把请求代理到 Spring Security 自己维护的多个过滤链,每个过滤链会匹配一些 URL,如果匹配则执行对应的过滤器。过滤链是有顺序的,一个请求只会执行第一条匹配的过滤链。Spring Security 的配置本质上就是新增、删除、修改过滤器。
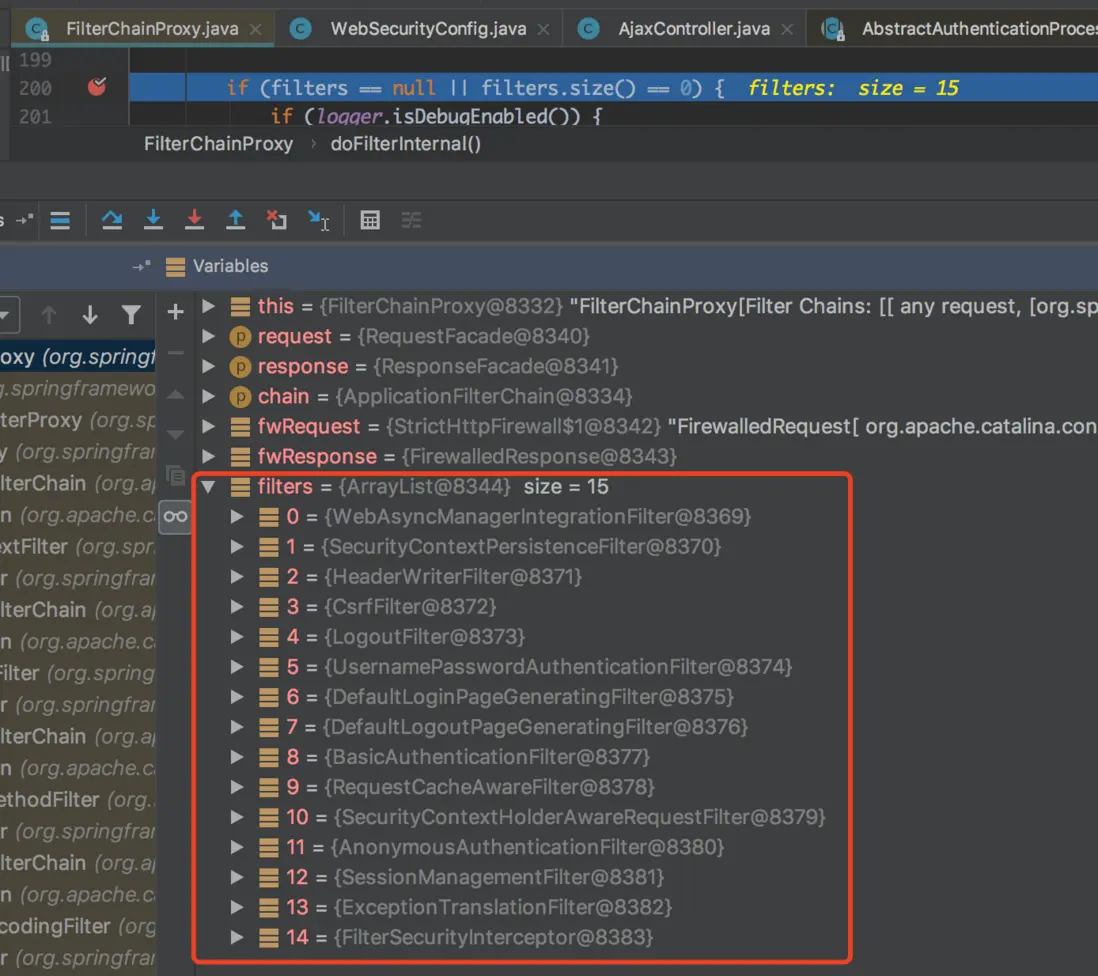
默认情况下系统帮我们注入的这 15 个过滤器,分别对应配置不同的需求。接下来我们重点是分析下 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 这个过滤器,他是用来使用用户名和密码登录认证的过滤器,但是很多情况下我们的登录不止是简单的用户名和密码,又可能是用到第三方授权登录,这个时候我们就需要使用自定义过滤器,当然这里不做详细说明,只是说下自定义过滤器怎么注入。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.addFilterAfter(...);
...
}
身份认证流程
在开始身份认证流程之前我们需要了解下几个基本概念
1.SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder 存储 SecurityContext 对象。SecurityContextHolder 是一个存储代理,有三种存储模式分别是:
- MODE_THREADLOCAL:SecurityContext 存储在线程中。
- MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL:
SecurityContext存储在线程中,但子线程可以获取到父线程中的SecurityContext。 - MODE_GLOBAL:
SecurityContext在所有线程中都相同。SecurityContextHolder默认使用 MODE_THREADLOCAL 模式,SecurityContext存储在当前线程中。调用SecurityContextHolder时不需要显示的参数传递,在当前线程中可以直接获取到SecurityContextHolder对象。
//获取当前线程里面认证的对象
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
//保存认证对象 (一般用于自定义认证成功保存认证对象)
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
//清空认证对象 (一般用于自定义登出清空认证对象)
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
2.Authentication
Authentication 即验证,表明当前用户是谁。什么是验证,比如一组用户名和密码就是验证,当然错误的用户名和密码也是验证,只不过 Spring Security 会校验失败。
Authentication 接口
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
//获取用户权限,一般情况下获取到的是用户的角色信息
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
//获取证明用户认证的信息,通常情况下获取到的是密码等信息,不过登录成功就会被移除
Object getCredentials();
//获取用户的额外信息,比如 IP 地址、经纬度等
Object getDetails();
//获取用户身份信息,在未认证的情况下获取到的是用户名,在已认证的情况下获取到的是 UserDetails (暂时理解为,当前应用用户对象的扩展)
Object getPrincipal();
//获取当前 Authentication 是否已认证
boolean isAuthenticated();
//设置当前 Authentication 是否已认证
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated);
}
3.AuthenticationManager ProviderManager AuthenticationProvider
其实这三者很好区分,AuthenticationManager 主要就是为了完成身份认证流程,ProviderManager 是 AuthenticationManager 接口的具体实现类,ProviderManager 里面有个记录 AuthenticationProvider 对象的集合属性 providers,AuthenticationProvider 接口类里有两个方法
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
//实现具体的身份认证逻辑,认证失败抛出对应的异常
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
//该认证类是否支持该 Authentication 的认证
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}
接下来就是遍历 ProviderManager 里面的 providers 集合,找到和合适的 AuthenticationProvider 完成身份认证。
4.UserDetailsService UserDetails
在 UserDetailsService 接口中只有一个简单的方法
public interface UserDetailsService {
//根据用户名查到对应的 UserDetails 对象
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}
5.流程
对于上面概念有什么不明白的地方,在们在接下来的流程中慢慢分析
在运行到 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器的时候首先是进入其父类 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 的 doFilter() 方法中
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
...
//首先配对是不是配置的身份认证的URI,是则执行下面的认证,不是则跳过
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
...
Authentication authResult;
try {
//关键方法, 实现认证逻辑并返回 Authentication, 由其子类 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 实现, 由下面 5.3 详解
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
// authentication
return;
}
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
//认证失败调用...由下面 5.1 详解
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
//认证失败调用...由下面 5.1 详解
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
//认证成功调用...由下面 5.2 详解
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
5.1 认证失败处理逻辑
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException failed)
throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
...
rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
//该 handler 处理失败界面跳转和响应逻辑
failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed);
}
这里默认配置的失败处理 handler 是 SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler,可自定义。
public class SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler implements
AuthenticationFailureHandler {
...
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException {
//没有配置失败跳转的URL则直接响应错误
if (defaultFailureUrl == null) {
logger.debug("No failure URL set, sending 401 Unauthorized error");
response.sendError(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value(),
HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.getReasonPhrase());
}
else {
//否则
//缓存异常
saveException(request, exception);
//根据配置的异常页面是重定向还是转发进行不同方式跳转
if (forwardToDestination) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to " + defaultFailureUrl);
request.getRequestDispatcher(defaultFailureUrl)
.forward(request, response);
}
else {
logger.debug("Redirecting to " + defaultFailureUrl);
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, defaultFailureUrl);
}
}
}
//缓存异常,转发则保存在request里面,重定向则保存在session里面
protected final void saveException(HttpServletRequest request,
AuthenticationException exception) {
if (forwardToDestination) {
request.setAttribute(WebAttributes.AUTHENTICATION_EXCEPTION, exception);
}
else {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null || allowSessionCreation) {
request.getSession().setAttribute(WebAttributes.AUTHENTICATION_EXCEPTION,
exception);
}
}
}
}
这里做下小拓展:用系统的错误处理 handler,指定认证失败跳转的 URL,在 MVC 里面对应的 URL 方法里面可以通过 key 从request或session里面拿到错误信息,反馈给前端
5.2 认证成功处理逻辑
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
...
//这里要注意很重要,将认证完成返回的 Authentication 保存到线程对应的 `SecurityContext` 中
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
//该 handler 就是为了完成页面跳转
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
这里默认配置的成功处理 handler 是 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler,里面的代码就不做具体展开了,反正是跳转到指定的认证成功之后的界面,可自定义。
5.3 身份认证详情
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
...
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY = "username";
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY = "password";
private String usernameParameter = SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY;
private String passwordParameter = SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY;
private boolean postOnly = true;
...
//开始身份认证逻辑
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
//先用前端提交过来的 username 和 password 封装一个简易的 AuthenticationToken
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
//具体的认证逻辑还是交给 AuthenticationManager 对象的 authenticate(..) 方法完成,接着往下看
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}
由源码断点跟踪得知,最终解析是由 AuthenticationManager 接口实现类 ProviderManager 来完成
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware,
InitializingBean {
...
private List<AuthenticationProvider> providers = Collections.emptyList();
...
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
....
//遍历所有的 AuthenticationProvider, 找到合适的完成身份验证
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
...
try {
//进行具体的身份验证逻辑, 这里使用到的是 DaoAuthenticationProvider, 具体逻辑记着往下看
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch
...
}
...
throw lastException;
}
}
DaoAuthenticationProvider 继承自 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 实现了 AuthenticationProvider 接口
public abstract class AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider implements
AuthenticationProvider, InitializingBean, MessageSourceAware {
...
private UserDetailsChecker preAuthenticationChecks = new DefaultPreAuthenticationChecks();
private UserDetailsChecker postAuthenticationChecks = new DefaultPostAuthenticationChecks();
...
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
...
// 获得提交过来的用户名
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
//根据用户名从缓存中查找 UserDetails
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
//缓存中没有则通过 retrieveUser(..) 方法查找 (看下面 DaoAuthenticationProvider 的实现)
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch
...
}
try {
//比对前的检查,例如账户以一些状态信息(是否锁定, 过期...)
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
//子类实现比对规则 (看下面 DaoAuthenticationProvider 的实现)
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
else {
throw exception;
}
}
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
//根据最终user的一些信息重新生成具体详细的 Authentication 对象并返回
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
//具体生成还是看子类实现
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal,
Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) {
// Ensure we return the original credentials the user supplied,
// so subsequent attempts are successful even with encoded passwords.
// Also ensure we return the original getDetails(), so that future
// authentication events after cache expiry contain the details
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
principal, authentication.getCredentials(),
authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities()));
result.setDetails(authentication.getDetails());
return result;
}
}
接下来我们来看下 DaoAuthenticationProvider 里面的三个重要的方法,比对方式、获取需要比对的 UserDetails 对象以及生产最终返回 Authentication 的方法。
public class DaoAuthenticationProvider extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider {
...
//密码比对
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
//通过 PasswordEncoder 进行密码比对, 注: 可自定义
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
}
//通过 UserDetailsService 获取 UserDetails
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
//通过 UserDetailsService 获取 UserDetails
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
//生成身份认证通过后最终返回的 Authentication, 记录认证的身份信息
@Override
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal,
Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) {
boolean upgradeEncoding = this.userDetailsPasswordService != null
&& this.passwordEncoder.upgradeEncoding(user.getPassword());
if (upgradeEncoding) {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
String newPassword = this.passwordEncoder.encode(presentedPassword);
user = this.userDetailsPasswordService.updatePassword(user, newPassword);
}
return super.createSuccessAuthentication(principal, authentication, user);
}
}
加密
在 Spring Security 中加密是一个很简单却又不能忽略的模块,数据只有加密起来才更安全,这样就散算据库密码泄漏也都是密文。
Spring Security 为我们提供了一套加密规则和密码比对规则,org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder 接口,该接口里面定义了三个方法。
public interface PasswordEncoder {
//加密(外面调用一般在注册的时候加密前端传过来的密码保存进数据库)
String encode(CharSequence rawPassword);
//加密前后对比(一般用来比对前端提交过来的密码和数据库存储密码, 也就是明文和密文的对比)
boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword);
//是否需要再次进行编码, 默认不需要
default boolean upgradeEncoding(String encodedPassword) {
return false;
}
}
该接口实现类有下面这几个
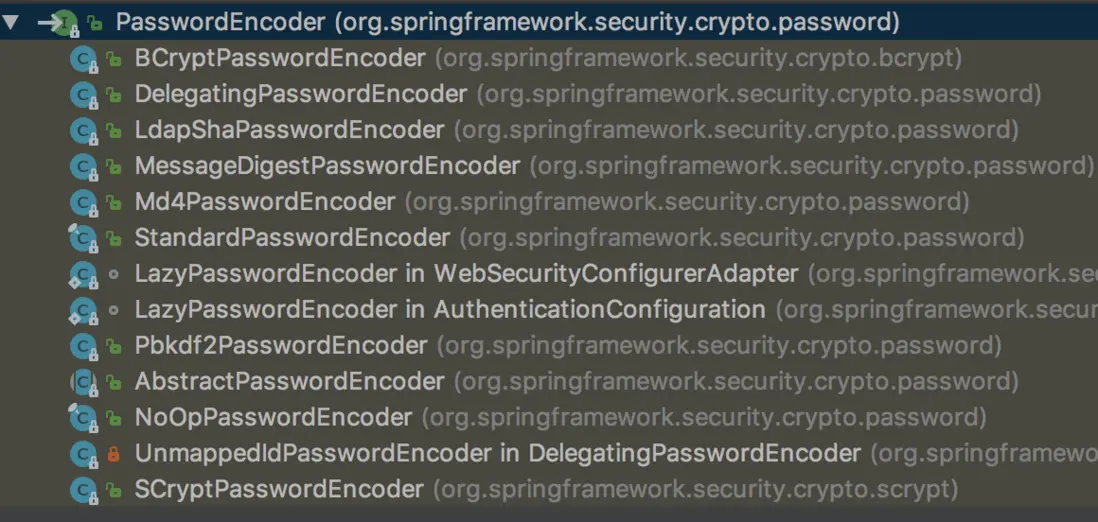
其中常用到的分别有下面这么几个
- BCryptPasswordEncoder:Spring Security 推荐使用的,使用 BCrypt 强哈希方法来加密。
- MessageDigestPasswordEncoder:用作传统的加密方式加密(支持 MD5、SHA-1、SHA-256…)
- DelegatingPasswordEncoder:最常用的,根据加密类型 id 进行不同方式的加密,兼容性强
- NoOpPasswordEncoder:明文, 不做加密
- 其他
MessageDigestPasswordEncoder
构造的时候需要传入算法字符串,例如 “MD5”、”SHA-1”、”SHA-256”…
String password = "123";
MessageDigestPasswordEncoder encoder = new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5");
String encode = encoder.encode(password);
System.out.println(encode);
System.out.println(encoder.matches(password,encode) == true ? "相等" : "不相等");
输出
{EUjIxnT/OVlk5J54s3LaJRuQgwTchm1gduFHTqI0qjo=}4b40375c57c285cc56c7048bb114db23
相等
调用 encode(..) 加密方法每次都会随机生成盐值,所以对相同的明文进行多次加密,每次结果也是不一样的。
从上面输出部分结合源码可以的出:加密的最终结果分为两部分,盐值 + MD5(password+盐值),调用 matches(..) 方法的时候先从密文中得到盐值,用该盐值加密明文和最终密文作对比。
BCryptPasswordEncoder
构造的时候可以传入哈希强度(strength),强度越大计算量就越大,也就意味着越安全,strength 取值区间[4-31],系统默认是 10。
String password = "123";
BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String encode = encoder.encode(password);
System.out.println(encode);
System.out.println(encoder.matches(password, encode) == true ? "相等" : "不相等");
输出
$2a$10$lxPfE.Zvat6tejB8Q1QGYu3M9lXUUpiWFYzboeyK64kbfgN9v7iBq
相等
调用 encode(..) 方法加密跟上面一样,每次都会随机生成盐值,密文也分为两部分,盐值和最终加密的结果,最终对比的时候从密文里面拿出盐值对明文进行加密,比较最终加密后的结果。
DelegatingPasswordEncoder
这是 Spring Security 推出的一套兼容方案,根据加密类型 id 字符串(idForEncode)去自身缓存的所有加密方式中(idToPasswordEncoder)取出对应的加密方案对象对明文进行加密和对应密文的对比,只是其密文前面都加上了加密方案 id 的字符串,具体的咱们看下面代码演示。
其初始化 Spring Security 提供了一个工厂构造方法
public class PasswordEncoderFactories {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static PasswordEncoder createDelegatingPasswordEncoder() {
String encodingId = "bcrypt";
Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap<>();
encoders.put(encodingId, new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("ldap", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.LdapShaPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD4", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.Md4PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD5", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5"));
encoders.put("noop", org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
encoders.put("pbkdf2", new Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("scrypt", new SCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("SHA-1", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-1"));
encoders.put("SHA-256", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-256"));
encoders.put("sha256", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.StandardPasswordEncoder());
return new DelegatingPasswordEncoder(encodingId, encoders);
}
}
这个工厂的静态构造方法把常用的几种方案都注入到缓存中,但是注入的 idForEncode 对应的却是 BCryptPasswordEncoder,这样系统就可以达到在新存储密码可以使用 BCryptPasswordEncoder 加密方案进行加密,但是对于数据库里面以前用其他方式加密的密码也支持比对。
String password = "123";
PasswordEncoder encoder = PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
String encode = encoder.encode(password);
System.out.println(encode);
System.out.println(encoder.matches(password, encode) == true ? "相等" : "不相等");
输出
{bcrypt}$2a$10$Bh23zGZ2YPOsORNexoowb.fX4QH18GEh13eVtZUZvbe2Blx0jIVna
相等
从结果中可以看出,相比原始的 BCryptPasswordEncoder 密文前面多了加密方式的 id。
当然也可以自定义构造方法,来制定 DelegatingPasswordEncoder 用其他的方案进行加密。
接下来我们将其指定使用 MD5 方式来加密密码看看结果
Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap<>();
encoders.put("MD5", new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5"));
DelegatingPasswordEncoder encoder = new DelegatingPasswordEncoder("MD5", encoders);
String encode = encoder.encode(password);
System.out.println(encode);
System.out.println(encoder.matches(password, encode) == true ? "相等" : "不相等");
输出
{MD5}{XYwuzP8/lL/a3ASzA9UVM4rFs8lbsLvEoa5ydKER844=}d7f919bfd94554150f8ab3a809209ee3
相等
相比原始的 MessageDigestPasswordEncoder也是密文前面多了加密方式的 id。
应用
先示范下使用系统的 UserDetailsManager 来演示下简单的注入
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true, jsr250Enabled = true)
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
super.configure(web);
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("liuchao")
.password("{bcrypt}$2a$10$S.hMD3oV60YRIj38lHRhP.e3DAu3OwmssE/u/p2GLqqZ3SVsZA77W")
.roles("admin","user")
.and()
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
}
@Bean(value = "passwordEncoder")
public PasswordEncoder delegatingPasswordEncoder() {
//构造 DelegatingPasswordEncoder 加密方案
return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
}
